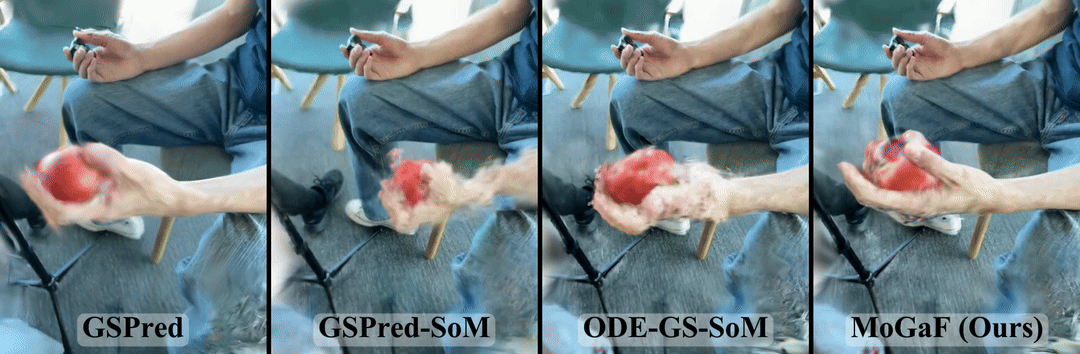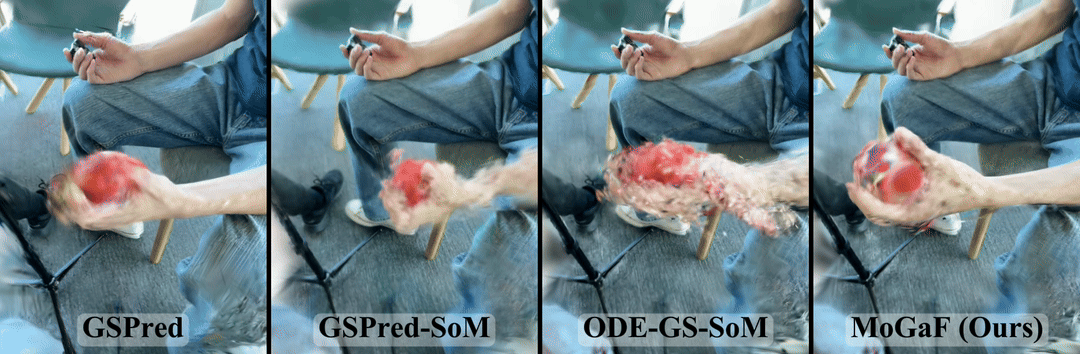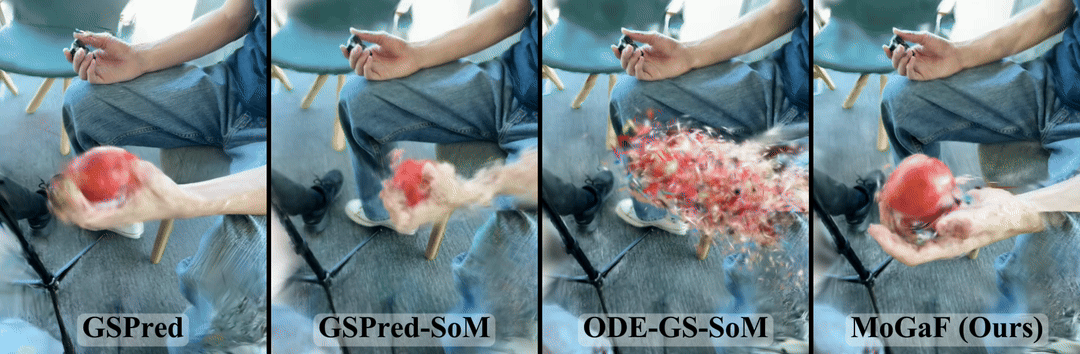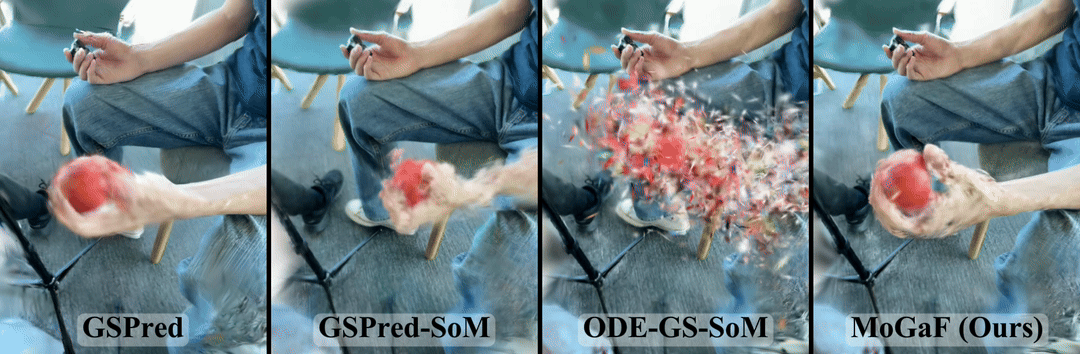
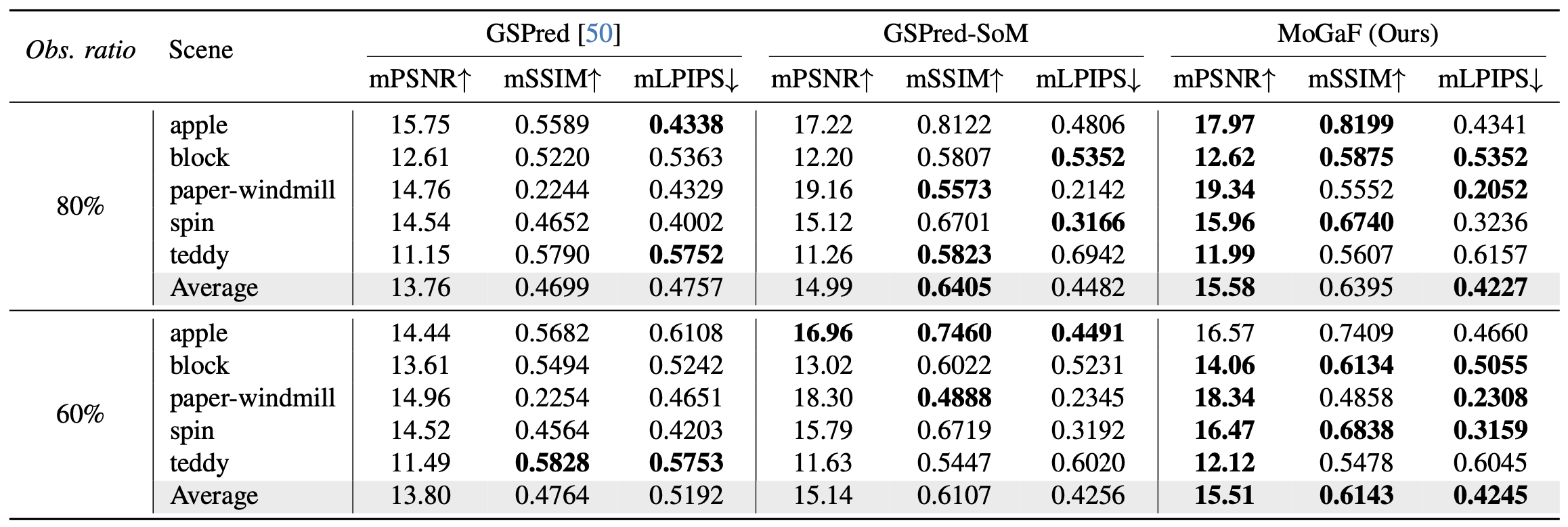
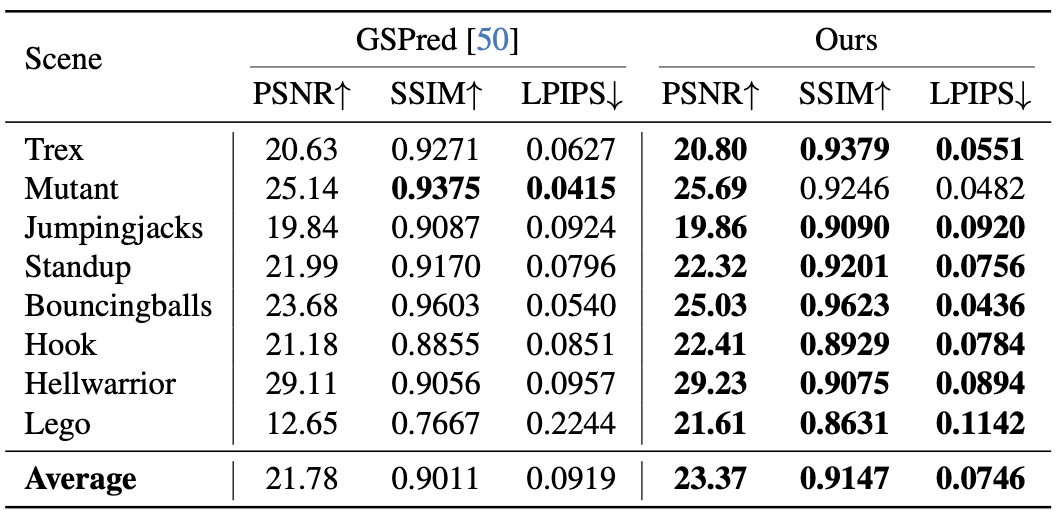
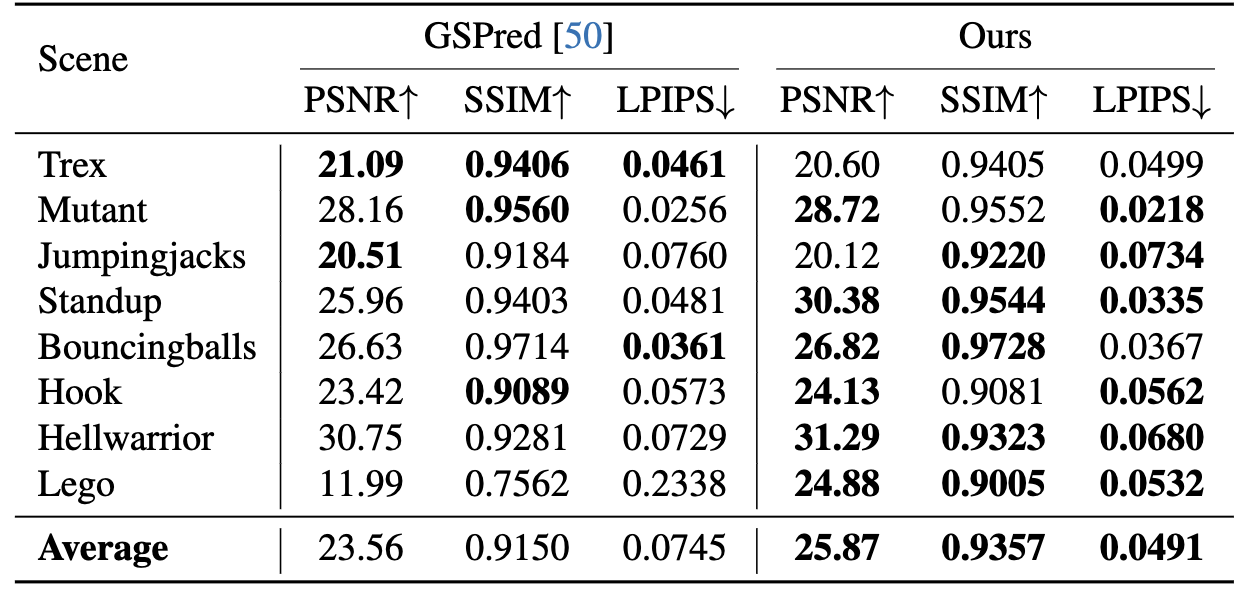
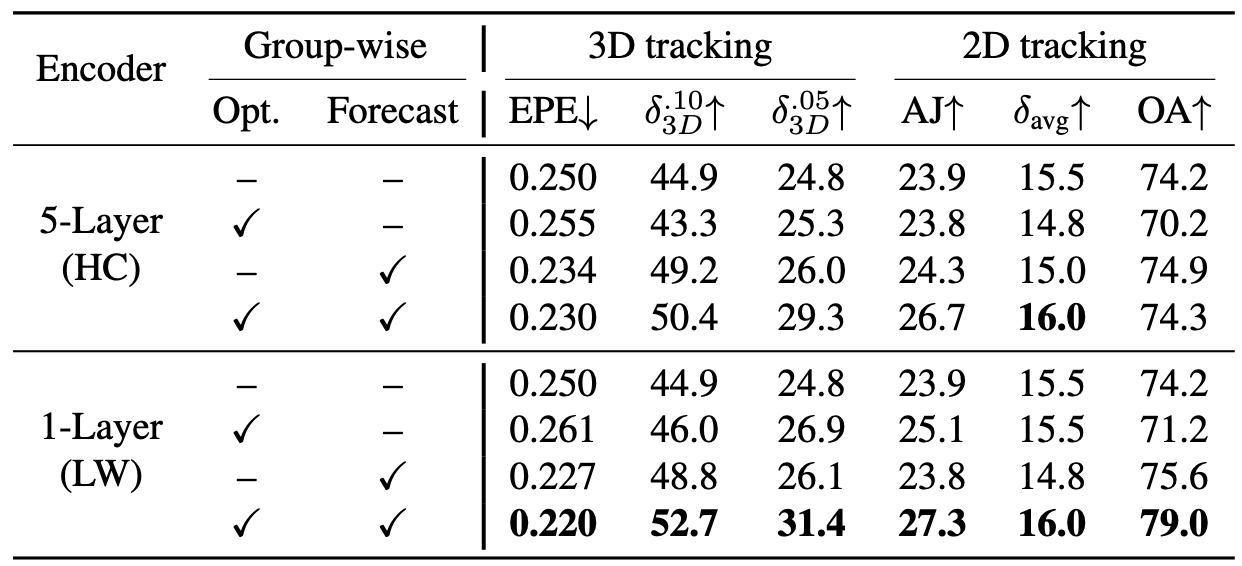
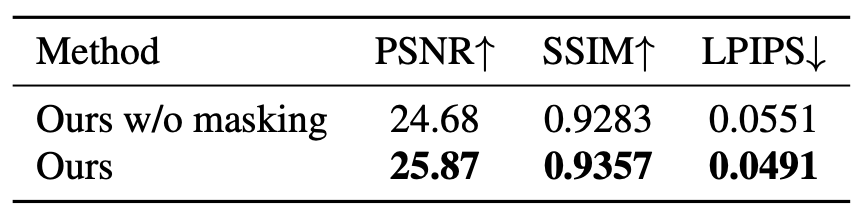
Main paper and supplementary results show that MoGaF consistently improves long-horizon forecasting quality by coupling group-aware optimization with future trajectory prediction. Quantitatively, the gains appear across both iPhone and D-NeRF benchmarks and are further supported by ablation trends: removing group-wise optimization harms tracking quality, while removing masking degrades future-frame fidelity. Qualitatively, MoGaF better preserves object-level motion coherence in dynamic scenes with complex non-rigid behavior. This is most visible in longer rollouts where local Gaussian drift accumulates for weaker baselines.
As discussed with supplementary qualitative evidence, MoGaF still has limitations under challenging long-horizon extrapolation: when future motion is highly ambiguous, partially occluded, or rapidly non-rigid, prediction uncertainty accumulates and can cause temporal drift, local over-smoothing, and occasional structural artifacts in fine object regions. These failure patterns become more visible as the forecast horizon grows far beyond the observed context, indicating that long-term stability under severe motion ambiguity remains an open problem.